Key Takeaways
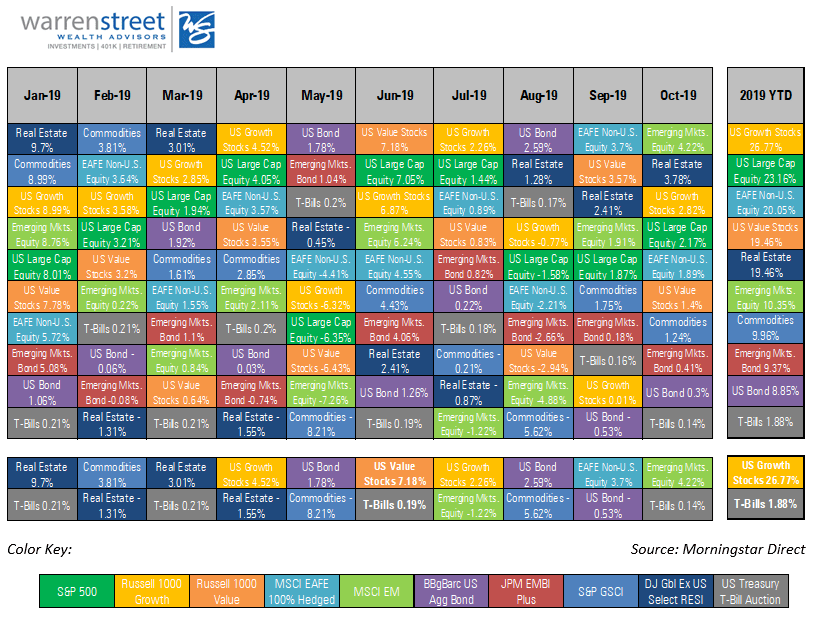
- The U.S. economy just exceeded the record for the longest business cycle expansion since economists started recording expansions in the 1930s (120 months plus 1 day)
- Global trade tensions are impacting manufacturing sectors all around the world; only the U.S. and France show continued expansion, with Germany falling the most
- Despite these concerns, June 2019 was among the strongest months for the U.S. stock market since 1955, driven largely by the FOMC decision to keep interest rates low and expectations of moderating trade tensions between the U.S. and China
- An astonishing 100% of futures markets participants expect the Fed to cut the Federal Funds rate between 0.25% and 0.50% in July. Conventional wisdom states that when 100% of market participants expect something, it’s time for rational investors to exit.
- Conclusion: Forecasts for multiple cuts in the Federal Funds rate are overdone; investors should be prepared for the stock market to react badly if expected rate cuts don’t materialize in July.
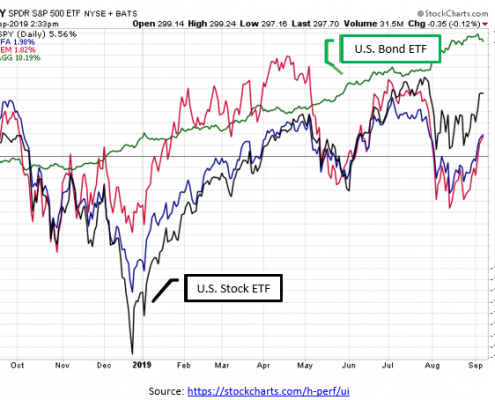
When the FOMC announced they would not raise the Federal Funds rate in June, global stock markets cheered.
Despite continuing uncertainty about trade tariffs, the decision not to raise rates was a relief to investors. Stock prices in both Europe and the U.S. jumped immediately after the announcement and held their gains through the rest of the week. Treasury bond prices rallied as well, bringing the 10-year interest rate below 2% for the first time since November 2016.
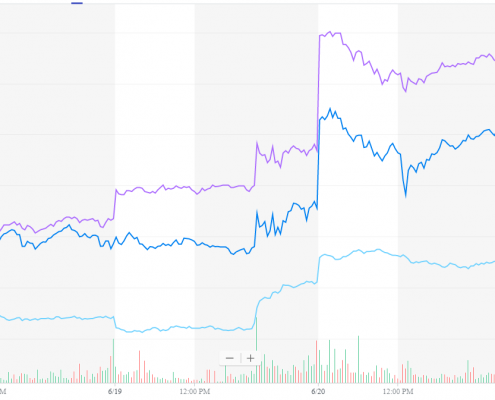
Source: finance.yahoo.com
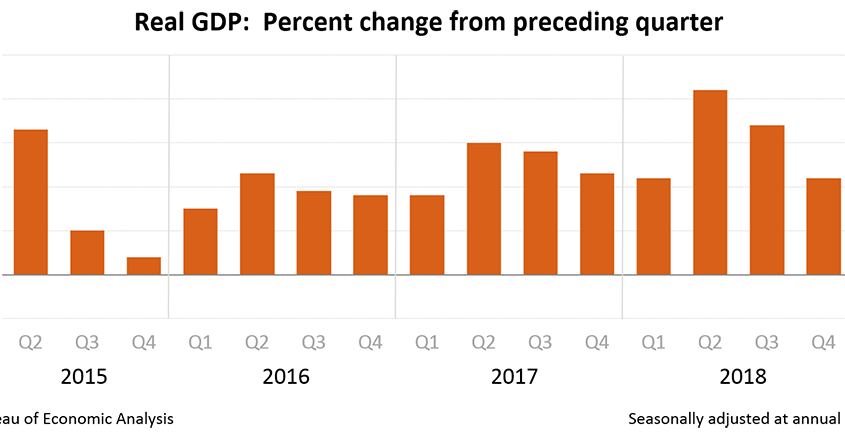
This enthusiasm may be warranted as the U.S. economy has reached the longest expansion since economists started recording expansions in the 1930s (120 months plus 1 day), edging past the expansion of 1991 to 2001.
But the markets seem a bit schizophrenic lately in their response to economic data.
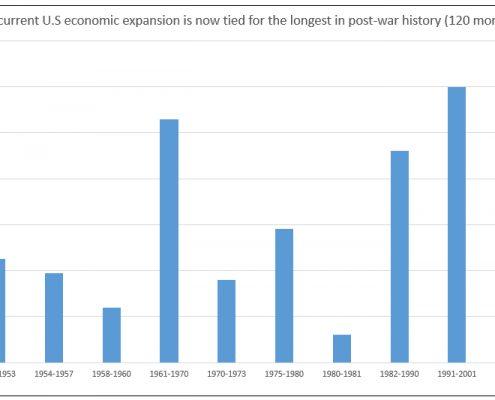
Longest expansion since 1930s
After their meeting in mid-June, Federal Reserve officials indicated that monetary policy can remain accomodative because concerns about a weakening economy had increased.
Here is the schizophrenic part: If the economy is indeed slowing, shouldn’t the stock market be cautious since corporate profits are expected to slow? But despite a few bad days and weeks from time to time, the U.S. stock market has hit new highs in 2019. If the Fed becomes more confident about the economy and raises interest rates slightly, this should signal stronger future corporate profits and boost the stock market. But instead of cheers, the prospect of the Fed continuing to ‘normalize’ short-term interest rates has been met with stock market tumbles.
This fearful reaction might be based on historical precedents which are no longer relevant. Some past expansions were indeed derailed by the Fed increasing rates too much. But the last 3 recessions in the U.S. were not sparked by interest rate increases but by market excesses: the Dot Com boom and bust in 1999-2000 and the housing price bubble in 2007-2008 being prime examples.
To better gauge when and if the economic expansion has run its course, investors would be wise to worry less about the Federal Funds rate and more about asset values, business activity, and the strength of labor markets.
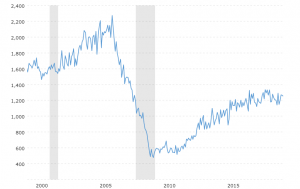
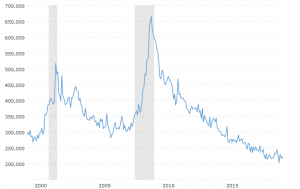
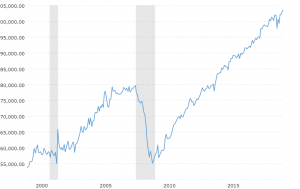
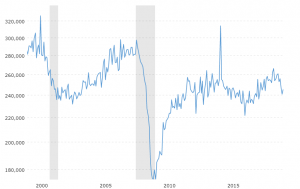
According to Dr. David Kelly, chief global strategist for J.P. Morgan Asset Management, the four key areas to watch in regard to ‘expansion killers’ are home building, business fixed investment, motor vehicle sales, and change in inventories.
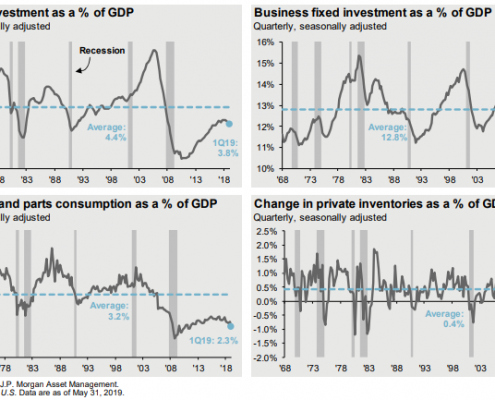
Dr. David Kelly’s ‘expansion killers’
Recessions since the late 90s have been associated less with interest rates and more with booms and busts in at least one of these areas. Since none of these factors are in ‘boom’ territory, it’s difficult to imagine a ‘bust’ scenario around the corner. As Dr. Kelly said, it’s hard to hurt yourself when jumping out a basement window.
The only leading indicator sitting on the second floor – rather than the basement – is the level of U.S. stock prices relative to earnings. As reported by Ned Davis Research, S&P 500 valuations in June were higher than average, but not by much. Whether you look at current earnings or forward earnings projections, the stock market seems to be fairly valued.
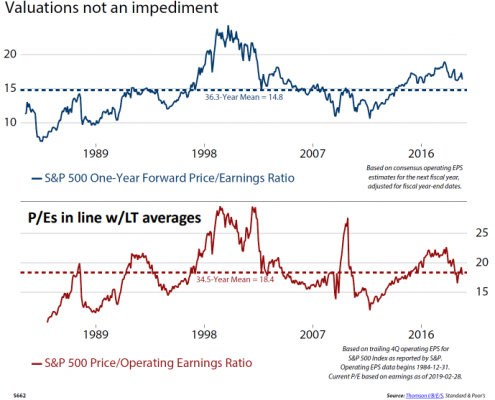
U.S. stock market valuation seems fair
In any case, the Fed may have less ability to influence the economy than people think.
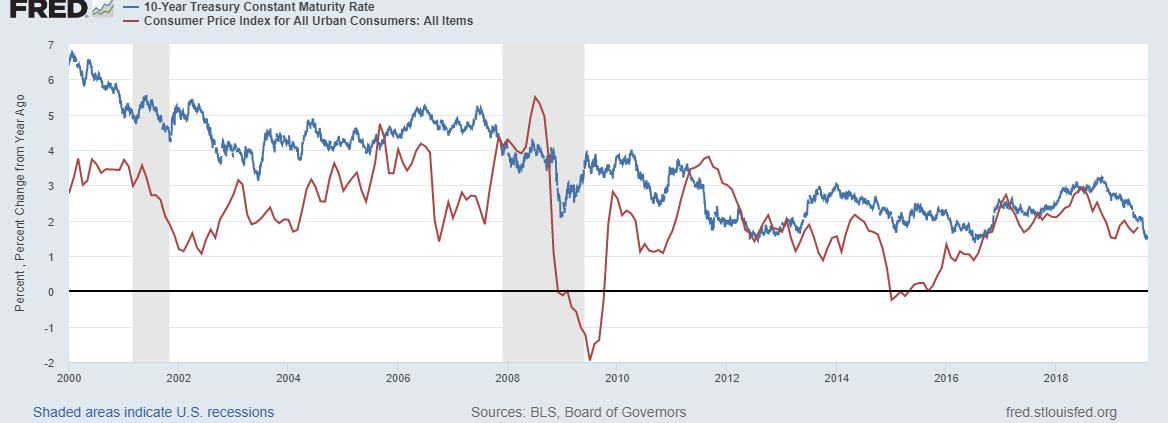
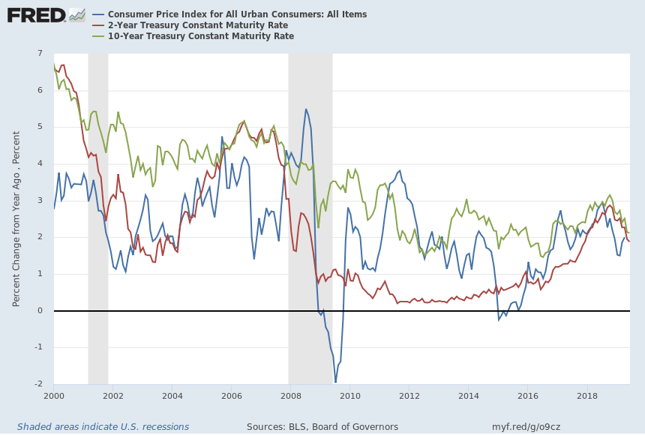
These days inflation seems more responsive to changes in global dynamics such as oil prices rather than domestic economic factors. Changing the Federal Funds rate isn’t likely to make much difference in the current economic environment.
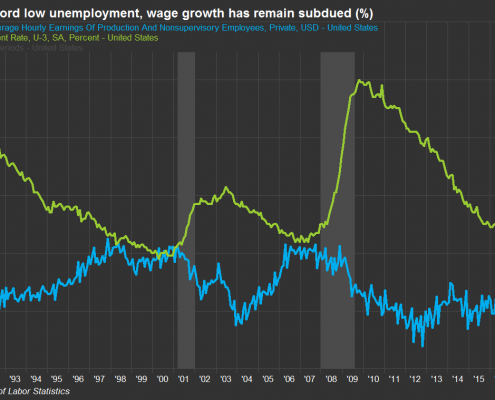
Low wage growth keeps inflation under control
Despite record low unemployment, wage growth has remained subdued helping keep inflation low as participants have begun returning to the job market after being sidelined during the ‘Great Recession’ of 2008-2009.
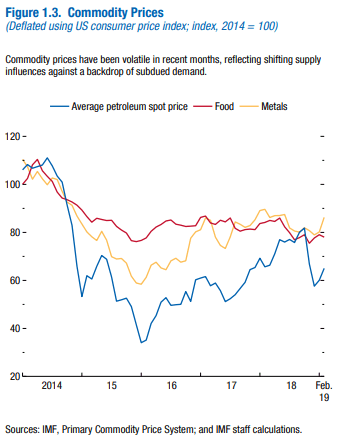
Range-bound oil prices are also putting downward pressure on inflation. OPEC has been trying to limit oil production for 2 years now, with mixed results. Their goal is to balance excess supply with less demand given the slowing Chinese economy, tariffs, and other political concerns. Despite these efforts, oil supplies are plentiful and prices remain restrained.
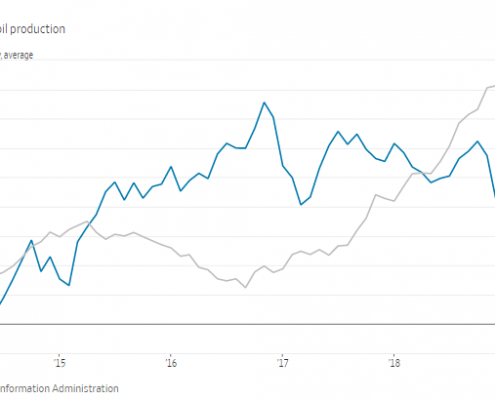
U.S. oil production offsets OPEC cuts
Has the Fed done too much? Or perhaps too little? When looking at the Federal Funds rate from a historical perspective, the FOMC has been extraordinarily cautious in its pace of increasing interest rates. Fed governors could certainly make a mistake, but it seems like their slow and steady pace is a wise approach for the foreseeable future. There’s no urgent need to raise rates, and limited value in lowering rates.

FOMC has been cautious ‘normalizing’ interest rates
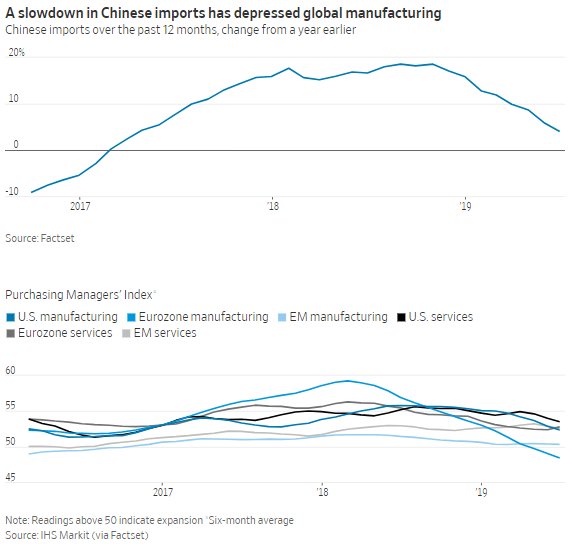
The primary risk to the global economy, particularly the manufacturing sector, isn’t interest rates but rather trade tensions. The U.S. and France are the only developed economies with manufacturing sectors still in expansion territory. Overseas, Germany’s manufacturing sector has fallen the most as much of its manufactured goods have traditionally been exported to the U.S. and other countries.
With most of the developed world struggling to stay in positive territory, global demand and supply dynamics are likely to keep U.S. inflation near or below the Fed’s 2% target indefinitely.
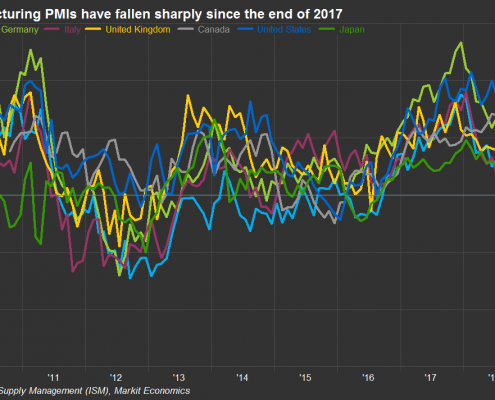
Global manufacturing feels the bite of tariffs
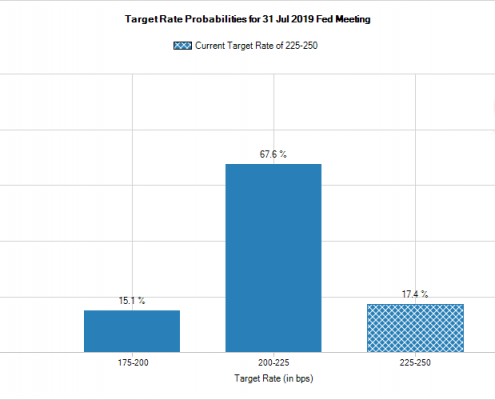
Despite the modestly positive economic landscape, an astonishing 100% of Eurodollar futures participants expect the Fed to cut the rates between 0.25% and 0.50% in July.
Since the Fed’s decision in June to keep interest rates the same, futures market participants began enthusiastically betting on not just one 0.25% cut, but two cuts in the Federal Funds rate when the FOMC meets in July. Conventional wisdom states that when 100% of market participants expect something, it’s time for rational investors to exit.
After the first flurry of press reports forecasting a rate cut in July, more Fed officials have been speaking publicly about their base case economic scenario being steady, not requiring a rate cut. In recent days futures markets have slowly begun migrating away from projecting two rate cuts in July to only one, but even one cut isn’t justified by the data…at least not yet.
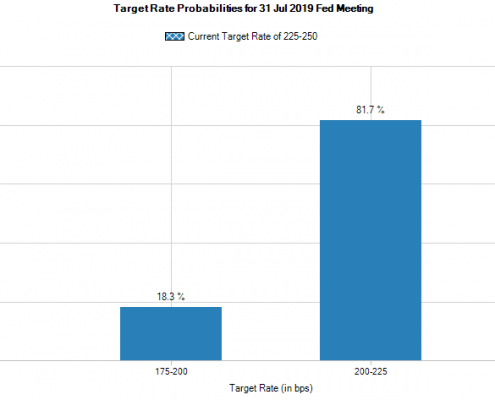
Futures expectations for July rate cuts
If we look forward to the end of the year, according to the CME Group ‘Countdown to FOMC’ as of July 1st over 13% of futures market participants think the Fed Funds rate will end the year between 2% and 2.25% (0.25% below the current level); another 13% believe the rate will be between 1.25% and 1.50% (1% below the current level!); and the median expectation is split with about 35% forecasting a Fed Funds rate between 1.5% and 1.75% (0.75% below the current level) and another 35% forecasting the Fed Funds rate to be between 1.75% and 2.0% by December (0.50% below the current level).
Barring a steep recession in the near term, expectations for multiple cuts in the Federal Funds rate are misguided. As my colleague at WSWA put it, the Fed is stuck in the unenviable position of a parent in the supermarket with a fractious child demanding candy before dinner. The right thing is to say No, but it’s difficult for both the parent (the Fed) and bystanders not to give in to the pressure.
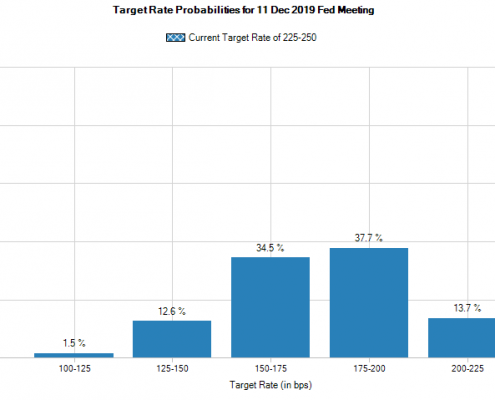
Futures forecast for rate hikes by December
With all this uncertainty, where can investors find good opportunities?
The answer is: In the global equity markets, particularly in Europe. The U.S. market should be fine going forward, but the best returns may have already come and gone. Though European economies are having a tough time right now, the European stock markets have been punished perhaps more than is warranted. In fact, the price of European stocks as of May 31st is less than 13 times compared to the U.S. stock market at close to 16 times earnings.
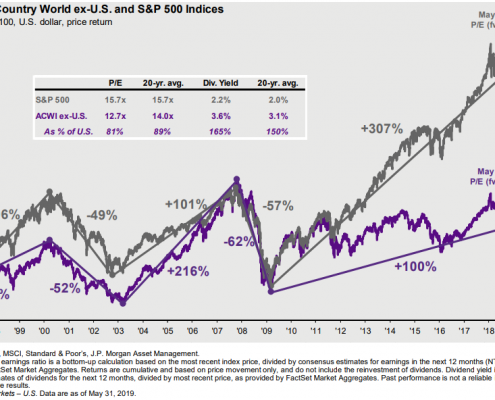
International stock valuation cheaper than U.S.
The way ahead in Europe is not going to be smooth, but long-term investors should consider dipping into international markets where stock valuations are more attractive. Overseas countries are generally behind the U.S. in their business cycles and have more growth to come.
Conclusion: Investors and the Fed should stay the course. Sometimes the best decision is to do nothing…for now.
Yes, the global economy is struggling right now. Corporations and governments have been issuing too much debt. Trade tensions and uncertainty make it difficult for businesses to develop long-term growth strategies. Political tensions across Europe and the U.K. are adding uncertainty to global economies.
Despite these concerns, the Fed should not lower interest rates. In fact, there is a case to be made to raise rates to balance outcomes between savers and speculators, plus keep some dry powder for the next recession.
Long-term investors should consider international assets. This is not the environment to make big bets either in or out of the financial markets. Instead, investors should stay engaged in the markets and be selective about segments likely to provide a reasonable risk/return profile over the remaining business cycle. With government bond yields extremely low and U.S. stock prices fully valued, carefully selected international securities may be the right choice for patient investors able to handle some bumps along the way.

Marcia Clark, CFA
Senior Research Analyst
DISCLOSURES
Investment Advisor Representative, Warren Street Wealth Advisors, LLC., a Registered Investment Advisor
The information presented here represents opinions and is not meant as personal or actionable advice to any individual, corporation, or other entity. Any investments discussed carry unique risks and should be carefully considered and reviewed by you and your financial professional. Nothing in this document is a solicitation to buy or sell any securities, or an attempt to furnish personal investment advice. Warren Street Wealth Advisors may own securities referenced in this document. Due to the static nature of content, securities held may change over time and current trades may be contrary to outdated publications.
Form ADV available upon request 714-876-6200



 Marcia Clark, CFA, MBA
Marcia Clark, CFA, MBA